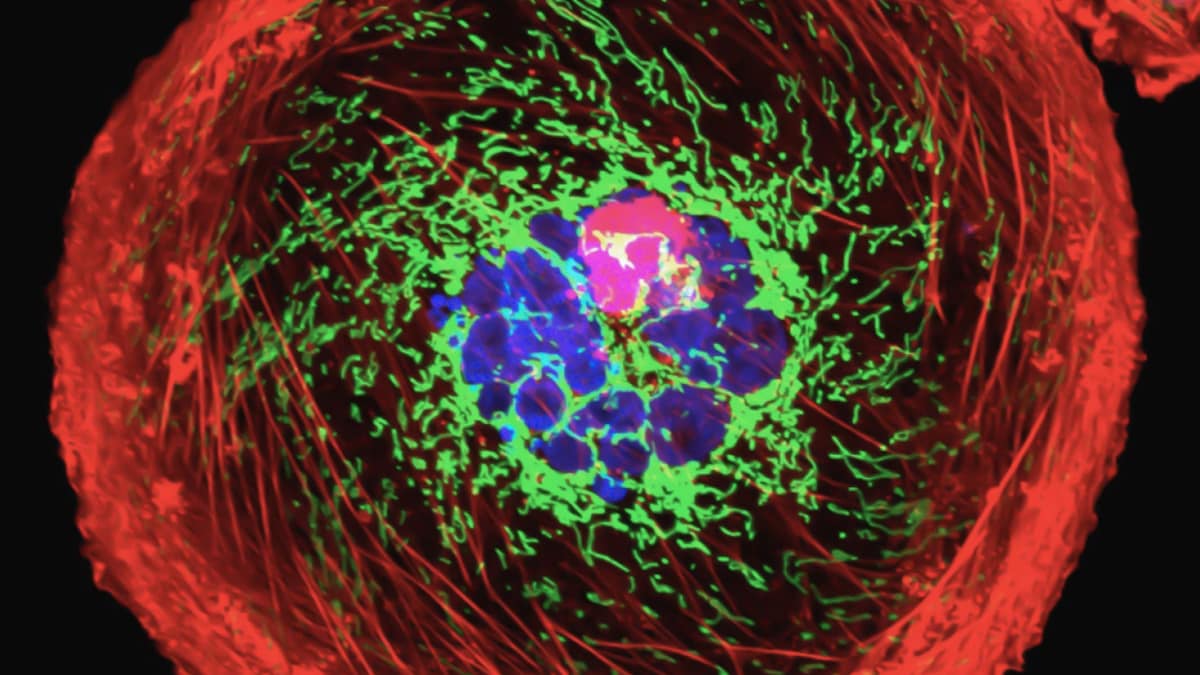
Researchers have uncovered a “division of labour” among mitochondria, with subpopulations within cells specialising in different roles when nutrients are scarce. Led by Dr. Craig Thompson, a cell biologist from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, the team observed that certain mitochondria in nutrient-deprived cells focus on producing energy, while others shift towards synthesising molecules necessary for cellular repair and protein production. This newfound specialisation could have an important role to play in how cells respond to injury and adapt to low-nutrient conditions.
Mitochondria: Beyond Energy Production
The study was published in Nature. Mitochondria are traditionally known for producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the molecule that powers most cellular processes. However, they are also involved in creating amino acids, essential for building proteins and other vital molecules. In resource-limited environments, such as when blood supply is reduced due to an injury, mitochondria may face constraints in simultaneously supporting energy production and molecular synthesis. Dr. Thompson’s research team sought to understand how cells might prioritise these functions under such conditions.
Mitochondrial Adaptation in Mouse Cells
The researchers cultured mouse cells under conditions forcing them to depend solely on mitochondrial ATP production, limiting alternative energy sources. Unexpectedly, the mitochondria continued to produce amino acids, suggesting a specialised adaptation mechanism. A key enzyme called P5CS was identified as instrumental in this process. Found in only certain mitochondria, P5CS enabled amino acid synthesis by clustering in specific organelles. Genetic modification that prevented this clustering blocked amino acid production, revealing P5CS’s essential role in the division of labour.
Implications for Cancer Research and Healing
The study’s findings may offer insights into how nutrient-deprived cancer cells sustain growth, as some human pancreatic cancer cells also displayed specialised mitochondria with P5CS clusters. Dr. Samantha Lewis, a mitochondrial biologist at the University of California, Berkeley, commented on the study, noting that it offers a model for examining mitochondrial diversity. Dr Martin Picard, a mitochondrial psychobiologist at Columbia University, highlighted the need for further research to assess the importance of this specialisation in living organisms, as this study was conducted in cultured cells.
For the latest tech news and reviews, follow Gadgets 360 on X, Facebook, WhatsApp, Threads and Google News. For the latest videos on gadgets and tech, subscribe to our YouTube channel. If you want to know everything about top influencers, follow our in-house Who’sThat360 on Instagram and YouTube.





